Ovarian Cyst Surgery: Things To Consider Before And After
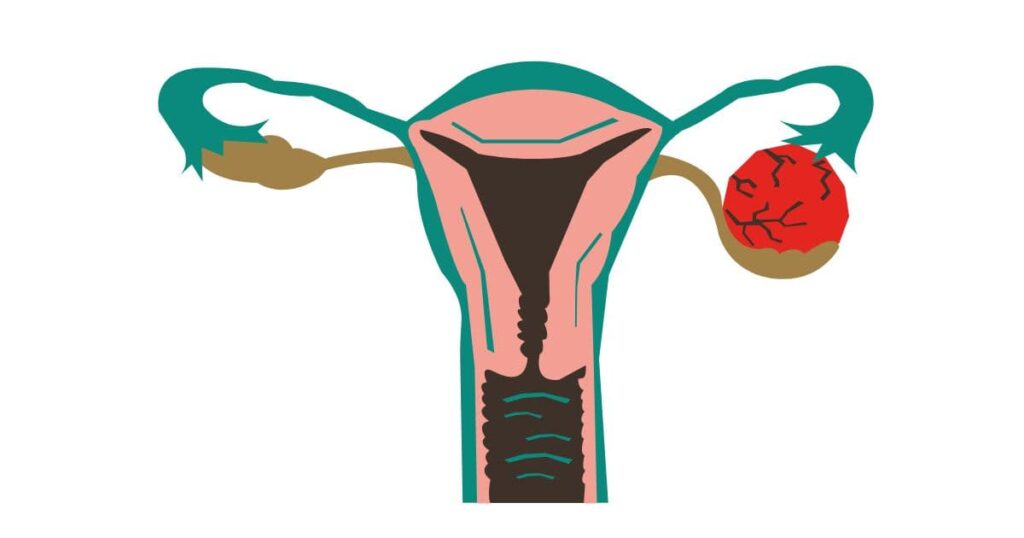
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop in or on the ovary. It can be seen in women of all ages. Ovarian cysts may continue to exist without causing symptoms in some women.
In some cases, it can cause problems such as pain, pelvic pressure, and menstrual irregularities. Since most ovarian cysts do not cause cancer, surgical intervention is not performed.
However, cysts that cause severe symptoms should be removed with ovarian cyst surgeries.
What Will We Learn?
What Are Ovarian Cyst Surgeries?
Ovarian cyst surgery is surgery to remove a single or multiple cysts from one or both ovaries. The type of surgery is planned depending on the degree of damage caused by the cysts.
In some cases, the cysts are large and occupy a large surface of the ovaries. In such cases, the entire ovary may need to be removed.
Why Is Ovarian Cyst Surgery Needed?
The problems that make ovarian cyst removal surgery necessary are listed below:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome: It is a very common condition. It is associated with the inability of the ovaries to release the egg to be fertilized by the sperm due to the abnormality in hormone levels. There are usually many small cysts on the surface of the ovaries. As the cysts grow in size, the symptoms worsen and surgery is required when drug therapy is not successful.
- Endometriosis: It is a condition in which the normal cells that make up the inner wall of the uterus move out of the uterus and accumulate in other organs. In this problem, also called chocolate cyst, blood tissues collect around the ovary and form a cyst. Surgical treatment is needed to treat endometriosis, which causes symptoms such as severe pain, and to remove the cyst.
- Cyst burst: Ovarian cysts may burst when they are large enough in size. Fluid from the cysts can spill into the pelvic cavity, causing serious complications and urgent surgery is required.
- Symptomatic cysts: Most of the time, ovarian cysts do not have any symptoms. However, if there are symptoms such as lower abdominal pain, frequent urination due to pressure on the bladder, abdominal swelling, nausea, vomiting, pain in the pelvic region during sexual intercourse, surgery should be performed.
- Ovarian cancer: Cysts in the ovary are usually not cancerous. However, in some cases, ovarian cancer may be present in the form of a cyst. Ovarian cancer surgery is required to remove the cysts.
What Is Done Before Ovarian Cyst Surgery?
Before ovarian cyst removal surgery, the procedure needs to be planned. Thus, it is ensured that the surgical process is successful and completed with minimal complications.
Ovarian cyst surgery is performed by gynecologists. The patient is informed by the gynecologist, and all the advantages and disadvantages are explained. What to do before and after the operation is explained in detail.
He or she must pass a series of tests to help determine the patient’s overall health. Blood tests are done to determine the white blood cell count, blood sugar, blood group determination, blood clotting and bleeding time.
If any medication is used for other health problems, this should be reported to the physician. Since anesthesia will be given, nothing should be eaten or drunk from the night before the surgery.
On the day of surgery, the patient must be prepared in advance. During the surgery, anesthesia is applied by wearing a clean, sterile surgical gown provided by the hospital.
The treatment area is cleaned with an antiseptic solution. Blood pressure, respiratory rate, pulse and body temperature are monitored during anesthesia and throughout the operation.
What Are The Types Of Ovarian Cyst Surgery?
Ovarian cyst surgeries can be performed with open or minimally invasive methods. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages, but both are equally effective.
Which method will be preferred is determined by the size of the cyst, its location, number and general condition of the patient.
How Is Open Ovarian Cyst Surgery Performed?
Also known as laparotomy, this method is an invasive surgical procedure. During laparotomy, the surgeon can correct structural problems.
It can remove tumors, areas of endometriosis, or scar tissue. It is used when the ovarian cyst is very large, when ovarian cancer is suspected, or when there are other problems with other organs.
If cancer is found, a larger incision is made, allowing the surgeon to closely examine the entire area, removing all cancerous growth more safely.
During the surgery, an incision is made in the skin of the lower abdomen of the patient. The underlying muscles, fascia, blood vessels are carefully separated.
When the ovaries and cyst are visualized, they are surgically cut, removed, or the tissues are burned with a laser beam.
The separated muscles are brought back to their original position. The incisions are closed by suturing.
Why Is Laparoscopic Ovarian Cyst Surgery Performed?
Laparoscopy operation is performed by making more than one small hole in the abdominal skin. With the help of small holes, surgical instruments are inserted into the abdominal cavity.
The abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas and a video camera is placed inside. Visualization of internal organs helps to gain greater precision when performing surgery.
Laparoscopy can also be used to confirm the diagnosis of an ovarian cyst in a woman of childbearing age.
Persistent, large, or painful ovarian cysts with no signs of cancer risk can be removed during laparoscopy. During this time, the ovary will not be damaged.
The most important advantage of this method is that the risk of infection is low and the recovery period is short.
How Is The Recovery Process After Ovarian Cyst Surgery?
Care should be taken a few days after ovarian cyst surgery to ensure rapid recovery with minimal complications.
After the operation, the patient is kept under observation for 1-2 days. Pain relievers, antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent any pain or infection.
After the surgery, the patient’s blood pressure, body temperature, pulse and respiratory rate are monitored regularly.
Nutritional status is maintained through serum, as he is not allowed to eat immediately afterwards. Food can be consumed after bowel movement resumes normally.
The patient is discharged when no complications occur after the observation. The surgical wound should be kept clean and dry.
The dressing should be changed as recommended by the surgeon.
If you have menstrual cramps, this article may help you.
