Are Ear Infections Contagious? Things To Pay Attention
Ear infections are a disease that anyone can experience at any age, be it children or adults.
A middle ear infection can occur as a result of an allergy, cold, sore throat, or respiratory infection.
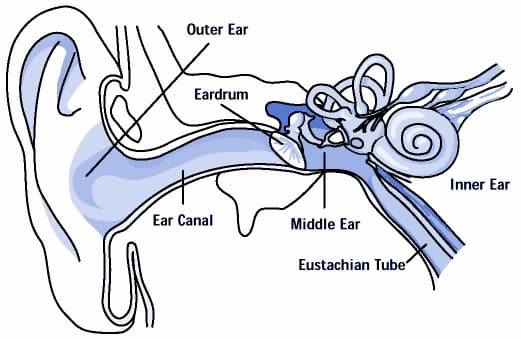
Obstruction of the Eustachian tube, which connects with the middle ear, paves the way for the formation of otitis media.
It can also occur in adults, but it is more common in children and is painful.
What Will We Learn?
What Is Acute Otitis Media?
Acute otitis media is the medical name for a common ear infection.
Media – means medium, Otitis – means ear infection.
It is a tube called the eustachian that connects the middle ear to the nose.
This tube functions to drain excess fluid from the middle ear.
In some cases of cold and flu, swelling in the nose prevents drainage.
These viruses and bacteria can enter the middle ear and cause a painful infection in the ear.
The infection causes an increase in fluid in the ear, which can cause irritability, fever, and pain.
What Are The Symptoms Of Otitis Media?
Symptoms of otitis media in adults may differ from those in children.
Middle ear inflammation, which is mostly seen in autumn and winter months, can heal on its own or get worse.
The symptom of otitis media in children is usually sudden onset of ear pain and fever after a cold.
Symptoms in infants are more like restlessness, fever, rubbing their ear against the pillow, or putting their hand to their ear.
In general, the symptoms of otitis media in children are as follows:
- Earache
- Trouble sleeping
- Malaise
- Restlessness and crying
- Hearing problems
- Loss of balance
- High fever
- Discharge from ear
- Loss of appetite
- Itching and irritation in and around the ear
Are Ear Infections Contagious?
No. Contrary to popular belief, ear infections are not contagious, but colds that cause ear infections are temporary.
If a cold that causes an ear infection passes to another adult or child, that person may also be at risk for an ear infection.
How Do You Know If Your Child Has An Ear Infection?
If your child is sick and has symptoms such as pain or irritability in the ear, your child may have an ear infection.
The most common causes of ear infections in children are usually colds and flu.
In some cases, earache may not be caused by an ear infection but by other factors such as a sore throat.
How Is An Ear Infection Diagnosed?
There is no type of diagnosis you can make at home or over the phone to diagnose an ear infection.
If you suspect an ear infection in your child, you should immediately take your child for examination to a doctor.
You can take your child to the examination within 24 hours.
But your doctor may tell you not to come to the emergency room in some cases.
While you wait for the office visit, you can give your child an aspirin-free pain reliever such as Acetaminophen or Ibuprofen to reduce pain and calm your child.
During the examination, your doctor will receive a brief information from you and will carefully check the appearance of the eardrum and the movement of the eardrum.
How Is An Ear Infection Treated?
Some studies have shown that a child’s ear infection can be cured without the use of antibiotics and without any side effects.
There are 2 types of treatment options in the treatment of ear infection.
These treatment options are called “watchful waiting” or the “observation option”.
Thanks to these methods, your child can be prevented from being exposed to unnecessary antibiotic use and its side effects.
In addition, the possibility of formation of “super bacteria” (antibiotic resistant bacteria) can be minimized.
Your child’s doctor will recommend a course of treatment based on symptoms and age.
If the observation option is to be used, the doctor’s recommendations should be strictly followed.
Do not forget that you should follow your doctor’s recommendations, even if antibiotic therapy is used.
Parents should not oppose the use of antibiotics prescribed by the doctor.
If antibiotics have been prescribed and the child is not allergic to penicillin, they will likely be given the antibiotic amoxicillin.
Depending on the severity of the disease, your doctor may prescribe this antibiotic for 5 days instead of 10 days.
As mentioned above, the use of antibiotics depends on the severity of the disease.
It is wrong to think that a single dose of antibiotics will cure an ear infection.
Antibiotics do not relieve pain, they only kill the viruses that cause the infection.
Painkillers that do not contain aspirin can be used for ear infection pain.
Even if you feel that your child is getting better, you should not stop the antibiotic treatment.
Make sure your child takes all antibiotics prescribed by your doctor.
How To Prevent Ear Infections In Children?
You can protect your children from ear infections by paying attention to the following factors:
- Teach your children to use a disposable tissue to cover their mouths when they sneeze, cough and blow their nose.
- Teaching your children that wipes should only be used once and then properly disposed of.
- Do not allow children to share toys they put in their mouths with other children.
- Wash toys that your children put in their mouths and play with thoroughly in hot and soapy water before giving them to other children.
- Teach your child to always wash their hands thoroughly after coughing and sneezing.
- Do not allow children with the flu or sick to share food and drink with each other.
- Thoroughly wash and disinfect all communal playgrounds regularly.
Things To Pay Attention
- Breastfeeding reduces the risk of ear infections in babies.
- If your child is over 2 years old, make sure that your child does not lie flat while bottle feeding.
- Never allow smoking around your child, no matter who is around. Some fumes can increase children’s risk of ear infections. Even the smoke from wood stoves can make it difficult for babies to breathe and cause ear infections.
- Children in day care centers may catch ear infections and the common cold more quickly. Caring for a sick child at home may be the best choice, but sometimes this is not possible. Parents should work with daycare center staff to ensure proper hand washing and hygiene.
Against all these precautions, if your child gets an Ear infection, he or she should be examined by a doctor or paramedic.
If signs of infection occur, be sure to follow the treatment as your doctor has told you.
Our article on ovasitol, which is good for ovarian health, may also attract your attention.
