Uterine Prolapse: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment Methods
In women, the muscles and ligaments in the pelvic floor may weaken due to advancing age or childbirth.
This can cause problems such as bladder, rectum and uterine prolapse.
Uterine prolapse is a common condition. When the symptoms develop accordingly, an effective treatment planning is required.
What Will We Learn?
What Is Uterine Prolapse?
Uterine prolapse is the downward movement of the uterus from its normal position. It can occur with weakening or stretching of the tissues that support the uterus. This discomfort can affect a woman’s physical and sexual activity and quality of life.
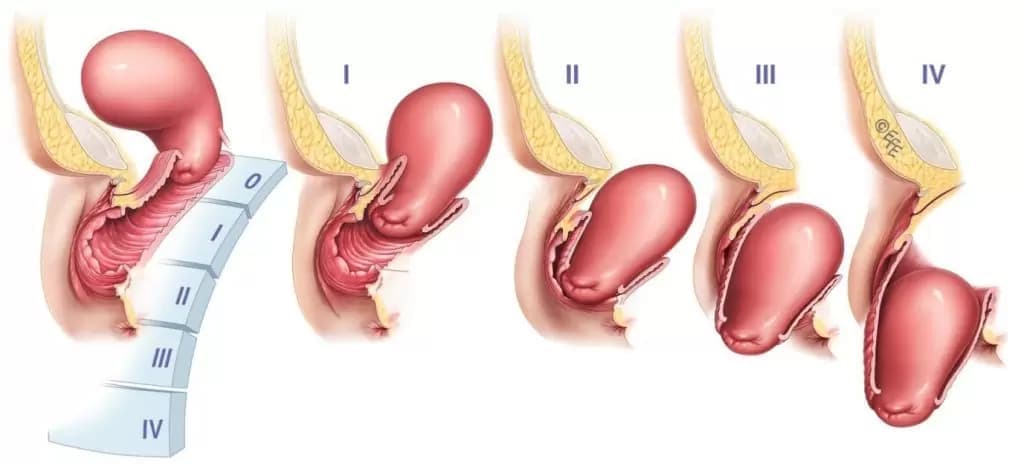
Uterine prolapse is classified according to 4 stages:
- The uterus is at the top of the vagina.
- The uterus has descended into the opening of the vagina.
- Part of the uterus is visible through the vagina.
- The uterus is completely out of the vagina.
What Are The Causes Of Uterine Prolapse?
The uterus, along with other organs in the pelvis, is supported by layers of pelvic floor muscles that hang like a hammock under the pelvis from side to side.
When these muscles, ligaments, and other pelvic tissues cannot provide their normal support, the uterus can be pushed down.
Factors that can cause uterine prolapse include:
- Vaginal delivery: Multiple and difficult normal deliveries are the biggest risk factor for uterine prolapse. This risk will increase if the baby is large, the pushing stage is prolonged during delivery, the use of forceps, and a third-degree tear is present.
- Pregnancy: The growth of the uterus is a factor that puts a significant strain on the pelvic floor.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese can lead to uterine prolapse.
- Menopause: Low estrogen levels that occur later in life can cause deterioration of muscles, ligaments and connective tissue, affecting the tissues that hold the uterus in place.
- Intra-abdominal pressure: Factors such as constipation, chronic coughing, and frequent heavy lifting can increase pressure in the abdomen and push the uterus down.
- Genetics: Some women may have inherited weakness of connective tissues.
What Are The Symptoms Of Uterine Prolapse?
If the uterine prolapse problem is in mild stages, no symptoms may be seen. Many women with this condition do not have any symptoms.
Common symptoms are:
- Urinary incontinence
- Inability to empty the bladder completely
- Feeling of heaviness or fullness in the pelvis area
- bloating in the vagina
- Backache
- Pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis
- Constipation
- Bleeding or discharge
- Repeated bladder infections
Symptoms usually decrease in the lying position and become less noticeable in the morning. It gets worse during the day or after exertion.
How Is uterine prolapse diagnosed?
In case of suspected uterine prolapse, a physical examination is performed to check the pelvis area.
Also, if there are problems with urinary incontinence or inability to empty the bladder, a procedure called cystoscopy may be performed to look at the bladder and urethra.
If further examination is required, tests such as an MRI or CT scan may be ordered.
The MRI procedure uses magnets and radio waves to create images.
CT scanning uses X-rays to create images. Thus, the kidneys and other pelvic organs can also be examined.
Is uterine prolapse risky if left untreated?
If the symptoms are not bothersome, uterine prolapse may not need to be treated. Problems can be resolved with some precautions and lifestyle changes.
- To be in the healthy weight range, weight must be lost.
- Heavy lifting or straining should be avoided.
- Chronic cough problem should be treated.
- Smoking should be stopped.
- Kegel exercises should be practiced.
If the symptoms are severe and the disturbances are at a high level, treatment is absolutely necessary.
How Is Uterine Prolapse Treated?
The problem of uterine prolapse can be treated with two different methods.
1. Vaginal Pessaries
A vaginal pessary is a flexible device inserted into the vagina to help hold sagging pelvic organs in place.
It is recommended for women who want to have children in the future or for those who do not want to have surgery.
Vaginal pessaries are often effective in relieving symptoms.
There are many types of pessaries, but the most common type are ring pessaries.
It is placed to support the cervix and uterus.
The pessary used in the right size is not felt and does not prevent sexual activity.
However, it is generally recommended to use a vaginal estrogen cream and remove it once a week at night.
There are few side effects associated with vaginal pessaries. It is possible for a pessary that is not the right size to come out of the vagina.
Rarely, it may cause pressure build-up in the vagina. If any discomfort, unusual vaginal bleeding or discharge occurs during use, the doctor should be notified.
Pessaries should be changed regularly every 3 to 6 months.
2. Surgical Methods
There are different types of surgery for the treatment of uterine prolapse.
Surgeries may include tissue repair or reconstructive surgery to support the pelvic organs.
Complete removal of the uterus is also an option.
Even after the operation, sagging in the same or a different pelvic organ can be repeated.
Urinary incontinence may occur due to stress incontinence after surgical operations.
However, surgical techniques improve quality of life.
How To Do Uterine Prolapse Exercises?
Kegel exercises help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
Doing Kegel exercises properly can reduce the risk of uterine prolapse.
Basic kegel exercises are very easy to perform.
To get started, practice initiating and stopping urination during the toilet can be done.
Kegel exercise should be done as follows:
- You should sit or lie down in a comfortable position.
- The muscles around the vagina and anus should be tightened, and the muscles should be felt as if they are being lifted.
- While breathing routinely, the contraction should be held for five seconds and released.
- This exercise should be repeated 10 times.
- Then the muscles should be tightened and released 10 times quickly.
- This exercise can be repeated three or more times a day.
